Pigmented lesions are remarkably common and the overwhelming majority are benign. Fotona has multiple wavelength as a result it effectively removes pigmented lesions. Fotona has the ability to produce very short pulses of intense light therefore they are selectively absorbed by treatment-specific pigments in a lesion.
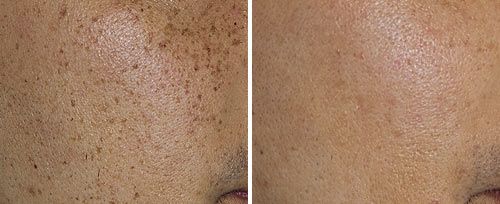
Fotona’s StarWalker laser system are the perfect tool for treating a wide range of pigmented lesions. Therefore enabling treatments for everything from moles and vascular lesions to ephelides, sunspots and melasma.
For a difficult-to-treat condition such as melasma, StarWalker and QX MAX are especially effective. This treatment enables the breaking apart of pigments only and not cells. This means that pigment destruction can take place without ablating the skin. This is a unique feature that also allows other treatment possibilities, safe and effective removal.
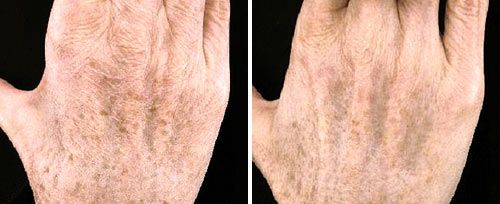
In addition Er:YAG lasers can also be used for the ablation of keratoses. Including moles, and other pigmented lesions. Therefore this enables the removal of the epidermis and superficial dermis in a controlled manner. Clinical studies have shown that Er:YAG lasers are effective for the treatment of keratoses. The clinical and histological improvement is up to 93% after just one treatment.
Superior Performance
High-energy single-nanosecond pulse technology is vastly more efficient at removing pigments than multiple-pulse lasers that generate equivalently high energies. The StarWalker’s and QX MAX’s high-energy, single-pulse Q-switched lasers allows larger spot sizes to remain effective by avoiding the scattering effect of laser light in skin tissue. With high-energy single pulses, deeper-lying pigments are targets and removed.
With high-energy laser pulses, the use of larger spot sizes is enabled, requiring less fluence to be effective. It’s important to note that while non-invasive procedures like Fotona Pigmented lesions removal can provide noticeable improvements, the results of non-invasive procedures can also vary depending on individual factors.

If you are unsure about your coverage, our team is happy to assist you in verifying your benefits.
Contact us today to learn more or schedule a consultation!